

Thieme整形外科期刊Seminars in Plastic Surgery的影响因子2020提高到了2.314。非常感谢所有作者、审稿人和编辑的支持和最宝贵的贡献。
以下三篇是被引用次数最多的论文,它们对影响因子的提高有着重要贡献,欢迎免费阅读。
Schaverien et al.
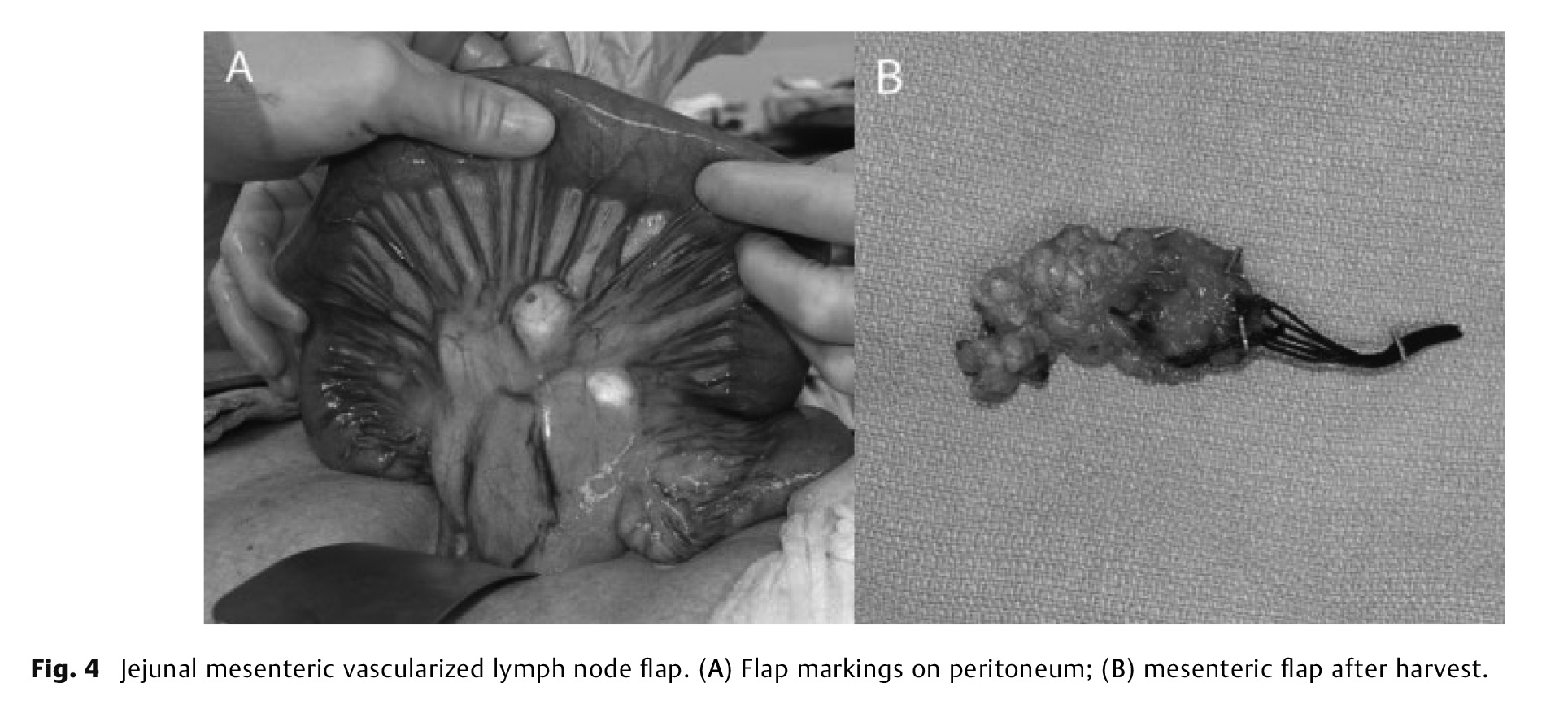
Advances in our understanding of the lymphatic system and the pathogenesis of lymphedema have resulted in the development of effective surgical treatments. Vascularized lymph node transfer (VLNT) involves the microvascular transplantation of functional lymph nodes into an extremity to restore physiological lymphatic function. It is most commonly performed by transferring combined deep inferior epigastric artery perforator and superficial inguinal lymph node flaps for postmastectomy breast reconstruction. For patients who do not require or are unable to undergo free abdominal breast reconstruction or have lymphedema affecting the lower extremity, several other VLNT options are available. These include flaps harvested from within the axillary, inguinal, or cervical lymph node basins, and lymph node flaps from within the abdominal cavity. This article reviews the lymph node flap options and techniques available for VLNT for lymphedema.
Anatomy of the Lymphatic System and the Lymphosome Concept with Reference to Lymphedema
Suami, Scaglioni
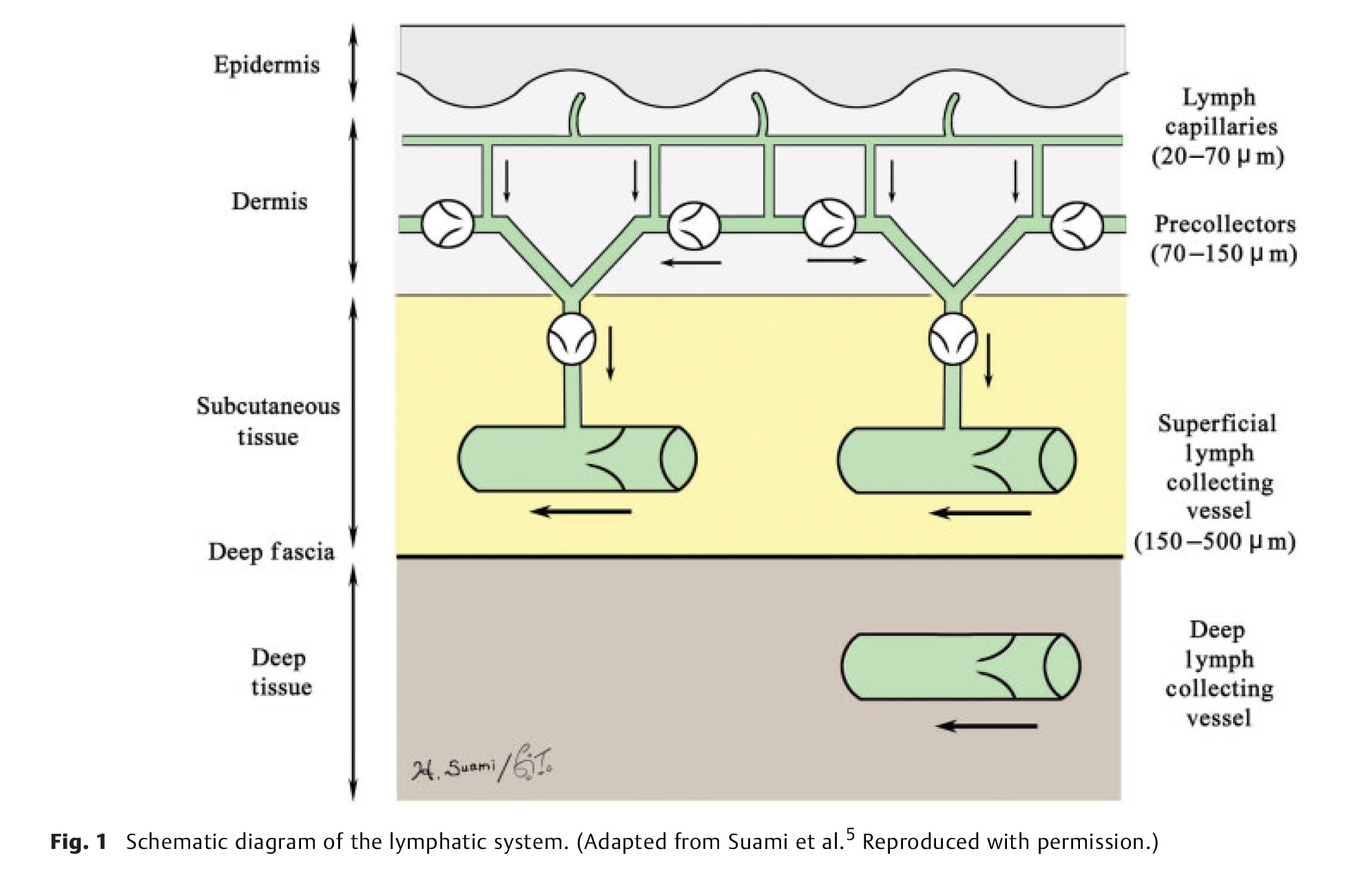
Precise knowledge of the lymphatic system normal anatomy is essential for understanding what structural changes occur in patients with lymphedema. In this article, the authors first review previous anatomical studies and summarize the general anatomy of the lymphatic system and lymphatic pathways in the upper and lower extremities. Second, they introduce their new anatomical concept, the “lymphosome,” which describes how the lymphatic vessels in a particular region connect to the same subgroup of regional lymph nodes. In addition, they describe the anatomical relationship between the perforating lymphatic vessels and arteries. In the last section, they explain the anatomical changes in the lymphatics after lymph node dissection, with reference to secondary lymphedema.
Schaverien et al.
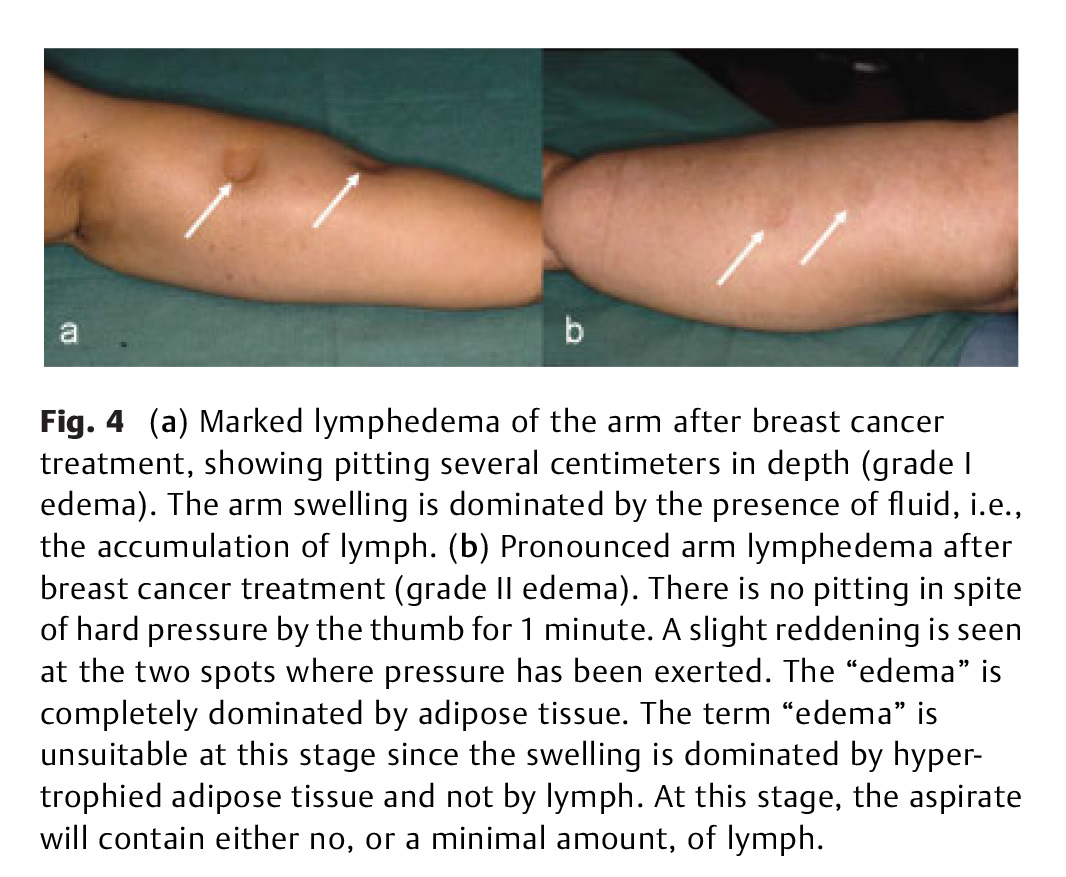
In the Western world, lymphedema most commonly occurs following treatment of cancer. Limb reductions have been reported utilizing various conservative therapies including manual lymph and pressure therapy, as well as by microsurgical reconstruction involving lymphovenous shunts and transplantation of lymph vessels or nodes. Failure of these conservative and surgical treatments to provide complete reduction in patients with long-standing pronounced lymphedema is due to the persistence of excess newly formed subcutaneous adipose tissue in response to slow or absent lymph flow, which is not removed in patients with chronic non-pitting lymphedema. Traditional surgical regimes utilizing bridging procedures, total excision with skin grafting, or reduction plasty seldom achieved acceptable cosmetic and functional results. Liposuction removes the hypertrophied adipose tissue and is a prerequisite to achieve complete reduction, and this reduction is maintained long-term through constant (24 h) use of compression garments postoperatively. This article describes the techniques and evidence basis for the use of liposuction for treatment of lymphedema.
阅读本刊更多论文,请点击这里。
